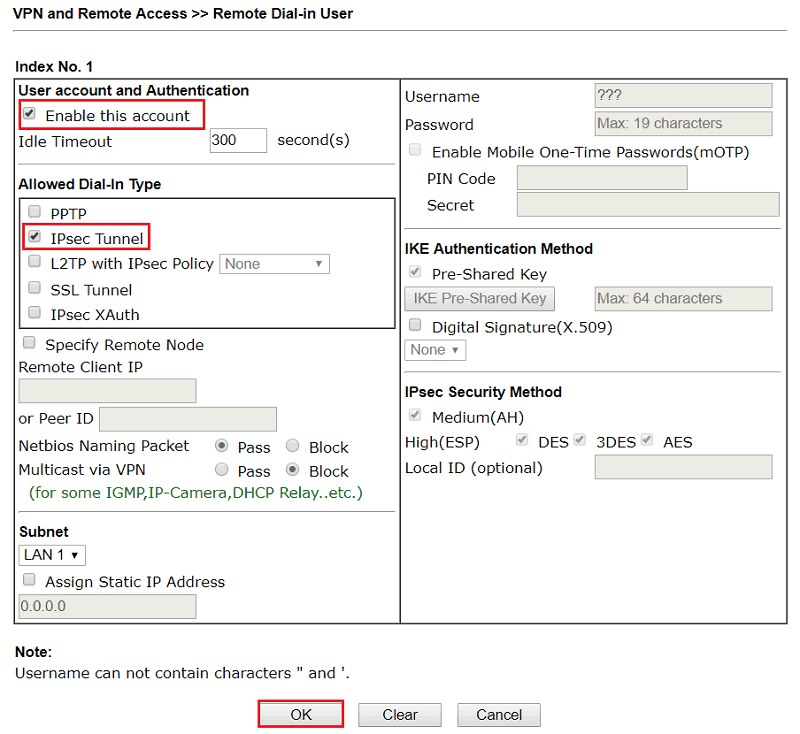
This section describes the process of configuring a site-to-siteconnection using a shared key style OpenVPN tunnel.
When configuring a shared key site-to-site OpenVPN connection one firewall willbe the server and the other will be the client. Usually the main location willbe the server side and the remote offices will act as clients, though theopposite is functionally equivalent. Similar to a remote access OpenVPNconfiguration there will be a dedicated subnet in use for the OpenVPNinterconnection between networks in addition to the subnets on both ends. Theexample configuration described here is depicted in FigureOpenVPN Example Site-to-Site Network.
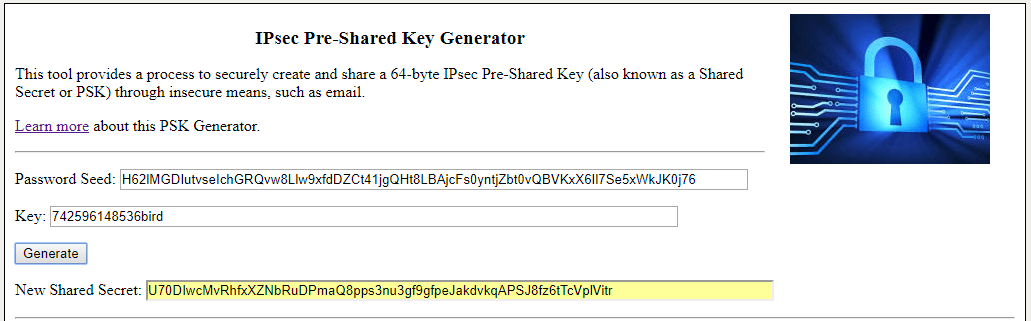
Other Password Tools. IPsec Pre-Shared Key Generator Quick Password List Large Password List Prime Length Passwords WordPress Salts. The length of pre-shared key is from 8 to 63 characters. Finding a key with random 20 characters by the brute force method is impossible at a convenient time unless the passphrase is in the dictionary. For the purpose of demonstration, we are going to brute force a passphrase with 9 characters.
- A pre-shared key setup allows you to login to the server (via SSH) without the need for a password and (optionally) only allows access to those users who can display the valid key to the server. They are as close to bulletproof as it gets for SSH. First, you will need a public/private key pair.
- GPG is a command-line tool that is used to provide digital encryption and signing services. It uses the OpenPGP standard. To generate a strong pre-shared key, you need to use its -gen-random option.
10.3.100.0/30 is used as the Tunnel Network. The OpenVPN tunnel betweenthe two firewalls gets an IP address on each end out of that subnet, asillustrated in the diagram. The following sections describe how to configure theserver and client sides of the connection.
Configuring Server Side¶
Navigate to VPN > OpenVPN, Server tab
Click Add to create a new server entry
Fill in the fields as follows, with everything else left at defaults:
Generate Pre Shared Key Online Games
Select Peer to Peer (Shared Key).
Enter text here to describe the connection (e.g. ExampleCoSiteBVPN)
Check Automatically generate a shared key, or paste in apre-existing shared key for this connection.
Generate Pre Shared Key Online
Enter the previously chosen network, 10.3.100.0/30
Enter the LAN on the Site B side, 10.5.0.0/24
Click Save
Click to edit the server that was created a moment ago
Find the Shared Key box
Select all text inside the Shared Key box
Copy the text to the clipboard
Save the contents to a file, or paste into a text editor such as Notepadtemporarily

Next, add a firewall rule on WAN allowing access to the OpenVPN server.
Navigate to Firewall > Rules, WAN tab
Click Add to create a new rule at the top of the list
Set Protocol to UDP
Set the Source address to match the client. If it has a dynamic IP address,leave it set to Any, otherwise set the rule to only allow from the WAN IPaddress of the client:
Select Single Host or Alias in Source
Enter the WAN address of the client as the Source address (e.g.
203.0.113.5)
Set the Destination to WAN Address
Set the Destination port to
1194in this instanceEnter a Description, such as
OpenVPNfromSiteBClick Save and the rule will look likeFigure OpenVPN Example Site-to-Site WAN Firewall Rule.
Click Apply Changes
A rule must also be added to the OpenVPN interface to pass traffic over theVPN from the Client-side LAN to the Server-side LAN. An “Allow all” style rulemay be used, or a set of stricter rules. In this example allowing all traffic isOK so the following rule is made:
Navigate to Firewall > Rules, OpenVPN tab
Click Add to create a new rule at the top of the list
Set Protocol to any
Enter a Description such as
AllowallonOpenVPNClick Save
Click Apply Changes
The server configuration is finished.
Configuring Client Side¶
Navigate to VPN > OpenVPN, Client tab on the client system
Click Add to create a new OpenVPN client instance
Fill in the fields as follows, with everything else left at defaults:
Select Peer to Peer (Shared Key).
Enter the public IP address or hostname of the OpenVPNserver here (e.g. 198.51.100.3).
Enter text to describe the connection (e.g. ExampleCoSiteAVPN)
Uncheck Automatically generate a shared key, then paste in theshared key for the connection using the key copied from the server instancecreated previously.
Must match the server side exactly (e.g. 10.3.100.0/30)
Enter the LAN network on the Site A side, 10.3.0.0/24
Click Save
A rule must also be added to the OpenVPN interface to pass traffic over theVPN from the Server-side LAN to the Client-side LAN. An “Allow all” style rulemay be used, or a set of stricter rules. In this example allowing all traffic isOK so the following rule is made:
Navigate to Firewall > Rules, OpenVPN tab
Click Add to create a new rule at the top of the list
Set Protocol to any
Enter a Description such as
AllowallonOpenVPNClick Save
Click Apply changes
The configuration of the client is complete. No firewall rules are required onthe client side WAN interface because the client only initiates outboundconnections. The server never initiates connections to the client.
Note
With remote access PKI configurations, typically routes and otherconfiguration options are not defined on the client configuration, but ratherthey are pushed from the server to the client. With shared key deployments,routes and other parameters must be defined on both ends as needed (asdescribed previously, and later inCustom configuration options), options cannot be pushedfrom the server to clients when using shared keys.
Testing the connection¶
Generate Pre Shared Key Online Login
The connection will immediately be active upon saving on the client side. Try toping across to the remote end to verify connectivity. If problems arise, referto Troubleshooting OpenVPN.